Exploring the Modern Aluminum Casting Factory: Innovation, Efficiency, and Production Power
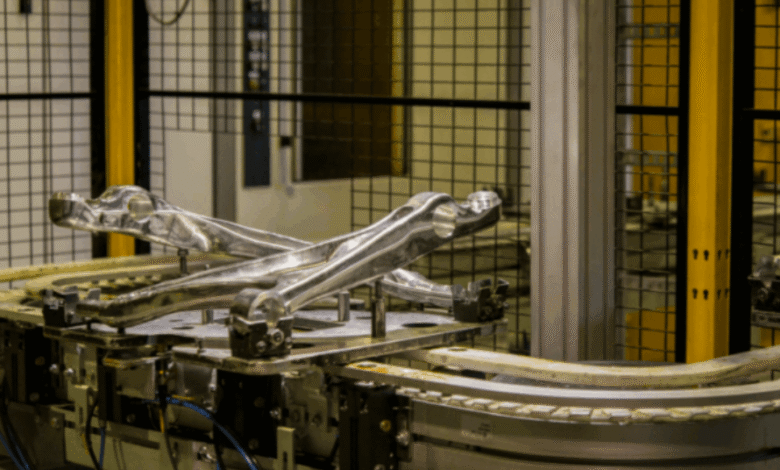

stands as a vital hub of engineering excellence. Whether it’s automotive parts, aerospace components, electrical housings, or household items, aluminum casting is the backbone of reliable, high-volume, and cost-effective production.
As industries across the globe push for lightweight materials, improved thermal conductivity, and corrosion-resistant designs, the demand for aluminum casting has soared. This article offers an in-depth look into how a typical aluminum casting factory operates, the technologies it uses, its role in global supply chains, and how to select the right factory partner for your production needs.
What Is an Aluminum Casting Factory?
An aluminum casting factory is a specialized industrial facility where molten aluminum is shaped into specific products by pouring it into molds. These factories can operate at various scales—from small workshops focusing on custom components to large-scale industrial facilities supplying thousands of identical parts daily.
These factories are equipped with melting furnaces, mold preparation units, casting lines, quality inspection labs, and post-processing areas. Many modern factories also integrate CNC machining, heat treatment, and surface finishing in-house, allowing them to deliver complete, ready-to-assemble parts to clients worldwide.
See also: tech innovations drive growth
The Core Processes Inside an Aluminum Casting Factory
A well-equipped aluminum casting factory typically handles the complete lifecycle of part production. Here’s how it unfolds:
1. Design and Prototyping
Before casting begins, the factory works with clients to create CAD designs and simulations. These digital models are used to make casting molds and identify potential design flaws using casting simulation software.
2. Mold Making
Molds can be permanent (metal) or expendable (sand, plaster, ceramic). Factories often have mold-making departments that create high-precision dies using CNC milling or additive manufacturing methods.
3. Melting and Pouring
Aluminum is melted in industrial furnaces at around 660°C. The molten metal is then poured into molds either manually or using automated ladling systems.
4. Solidification and Cooling
Once poured, the aluminum solidifies inside the mold. Cooling rates vary depending on part geometry and alloy composition. Faster cooling results in finer grain structures, improving strength.
5. Part Removal and Cleaning
After cooling, the castings are removed from molds, cleaned of residual sand or shell material, and trimmed of any excess metal (such as runners or sprues).
6. Finishing and Machining
Most aluminum casting factory units include machining centers to finalize dimensions, bore holes, tap threads, or smooth surfaces. Finishing options can include anodizing, powder coating, painting, or polishing.
7. Quality Control and Testing
Strict quality assurance processes such as X-ray inspection, ultrasonic testing, tensile testing, and dimensional checks ensure that every part meets the required standards.
Applications of Aluminum Castings in Industry
Aluminum castings manufactured in these factories are widely used across multiple sectors:
🚗 Automotive
Transmission housings, engine brackets, cylinder heads, and wheel hubs are frequently cast in aluminum for strength and lightweight design.
🛩 Aerospace
Landing gear components, cabin fixtures, and satellite parts rely on precision-cast aluminum for reduced weight and high mechanical performance.
⚙️ Machinery
Pump housings, impellers, valve bodies, and motor enclosures are all typically manufactured in aluminum casting plants.
🏠 Consumer Products
Cookware, lighting equipment, fan blades, and appliance housings are often made with aluminum casting methods due to their durability and thermal performance.
📡 Electronics
Heat sinks, enclosures, and shielding components benefit from aluminum’s conductivity and ease of casting.
Advantages of Working With a Modern Aluminum Casting Factory
Partnering with a reputable aluminum casting factory offers several key benefits:
✅ Precision and Repeatability
Computer-controlled machinery and high-quality molds ensure every part is made to spec—even in large volumes.
✅ Cost Efficiency
Especially for medium-to-high production runs, aluminum casting delivers low per-unit cost with minimal waste.
✅ Material Versatility
Factories can use different aluminum alloys (like A356, A380, ADC12) to optimize for strength, corrosion resistance, or conductivity.
✅ Integrated Services
From mold design and casting to machining and surface treatment, many factories now offer complete solutions under one roof.
✅ Environmental Sustainability
Many facilities are shifting toward green manufacturing practices, including energy-efficient furnaces and aluminum recycling.
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Casting Factory
Selecting the right factory partner is crucial for ensuring product quality, timely delivery, and cost control. Here are some tips:
- Evaluate Experience: Choose a factory with a proven track record in your industry.
- Inspect Certifications: Look for ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (automotive), or AS9100 (aerospace) certifications.
- Request Samples: Before full-scale production, ask for samples to test quality, surface finish, and tolerance levels.
- Review Capacity: Can the factory handle your volume—whether it’s 100 pieces or 100,000?
- Ask About Materials: Ensure they can source and cast your preferred aluminum alloy.
- Inquire About Customization: Does the factory offer design support or value-added services like anodizing, painting, or assembly?
Innovations in the Aluminum Casting Factory Industry
With the advancement of Industry 4.0, aluminum casting factory operations are being revolutionized by automation, data analytics, and robotics. Here’s how:
- Smart Furnaces: Monitor temperature in real time to optimize melting.
- Robotic Pouring: Reduces human error and improves safety.
- Digital Twins: Simulate casting conditions for mold optimization.
- AI-Powered Inspection: Identifies surface defects more accurately than traditional methods.
- IoT Integration: Tracks material flow, tool wear, and maintenance needs to avoid downtime.
These innovations are transforming traditional casting into a highly data-driven and efficient industrial process.
Conclusion
The modern aluminum casting factory is no longer just a metal shop—it’s a sophisticated production center where innovation, automation, and craftsmanship come together to deliver high-performance components across every industry.
Whether you’re launching a new product or scaling up an existing one, partnering with the right aluminum casting factory can ensure your components are manufactured with precision, speed, and cost-efficiency. As industries continue to demand lighter, stronger, and more sustainable materials, aluminum casting remains an indispensable technology in global manufacturing.